GNSS
SBAS: Enhancing GNSS Accuracy
In our modern world, accurate and reliable navigation has become an integral part of numerous industries, from aviation and maritime to land transportation and surveying. To meet the growing demands for precise positioning, Satellite-Based Augmentation Systems (SBAS) have emerged as a key technological advancement. SBAS enhances the accuracy, integrity, and availability of Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS), such as GPS, GLONASS, and Galileo, by providing additional correction data. This article explores the features, benefits, and applications of SBAS, shedding light on its importance in today’s interconnected world.
What is SBAS?
SBAS refers to a system that augments the signals transmitted by GNSS satellites to provide real-time correction data. It leverages a network of ground-based reference stations, known as Wide Area Reference Stations (WRS), that collect data from GNSS satellites and transmit it to a Master Control Center (MCC). The MCC processes the data, calculates the correction information, and broadcasts it to users via geostationary satellites. By integrating this correction data into GNSS receivers, SBAS enables highly accurate positioning and navigation.
How Does SBAS Work?
SBAS operates by comparing the signals received from GNSS satellites with the known positions of the WRS. Any discrepancies in the signals indicate errors, which are then used to generate correction information. This correction data includes factors such as clock errors, satellite ephemeris, ionospheric delays, and other atmospheric effects. GNSS receivers equipped with SBAS capability receive these corrections and apply them to improve the accuracy of their position calculations.
Key Features of SBAS
Coverage Area
SBAS offers wide-area coverage, typically encompassing several countries or regions. This makes it particularly valuable for applications that require seamless navigation across large areas, such as international aviation and maritime operations.
Accuracy Enhancement
By providing precise correction information, SBAS significantly enhances the accuracy of GNSS positioning. The corrections address various error sources, including atmospheric effects and satellite clock errors, resulting in improved position accuracy.
Integrity Monitoring
SBAS incorporates integrity monitoring capabilities, which continuously assess the reliability of the GNSS signals. In case anomalies or errors are detected, the system can alert users and provide guidance on the trustworthiness of the received signals.
Availability and Continuity
SBAS strives to ensure high availability and continuity of service. By employing redundant ground and space infrastructure, it minimizes downtime and reduces the risk of service interruptions.
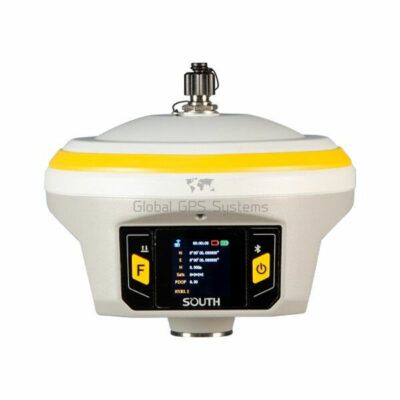
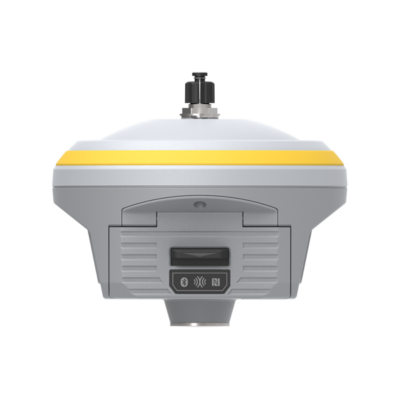
some popular receivers that support sbas
Benefits of SBAS
Enhanced Safety
SBAS plays a vital role in critical applications where safety is paramount, such as aviation. By providing accurate and reliable navigation data, it enables pilots to make informed decisions, enhances situational awareness, and reduces the risk of accidents.
Increased Efficiency
Industries reliant on precise positioning, such as (land) surveying, construction, and agriculture, benefit from the improved efficiency offered by SBAS. Accurate positioning minimizes errors, optimizes resource allocation, and streamlines operations, leading to cost savings and increased productivity.
Improved Navigation in Challenging Environments
SBAS is particularly valuable in environments where GNSS signals may be obstructed or degraded, such as urban canyons or dense forests. The correction data provided by SBAS compensates for these obstacles, enabling reliable navigation even in challenging conditions.
Global Compatibility
SBAS is designed to be compatible with multiple GNSS constellations, ensuring global coverage and interoperability. This compatibility enhances flexibility for users and promotes international cooperation in the field of navigation.

Applications of SBAS
Aviation
SBAS has revolutionized aviation navigation by providing precise positioning for aircraft. It supports various applications, including en-route navigation, approach and landing procedures, and runway guidance, enhancing flight safety and operational efficiency.
Maritime
In the maritime sector, SBAS enhances navigation accuracy for ships, enabling safer and more efficient passage through congested waterways. It also facilitates precise docking, pilotage operations, and search and rescue efforts.
Land Transportation
SBAS benefits land transportation by improving the accuracy of vehicle navigation systems, autonomous driving technologies, and fleet management solutions. It enables reliable routing, reduces travel times, and enhances the overall efficiency of transportation networks.
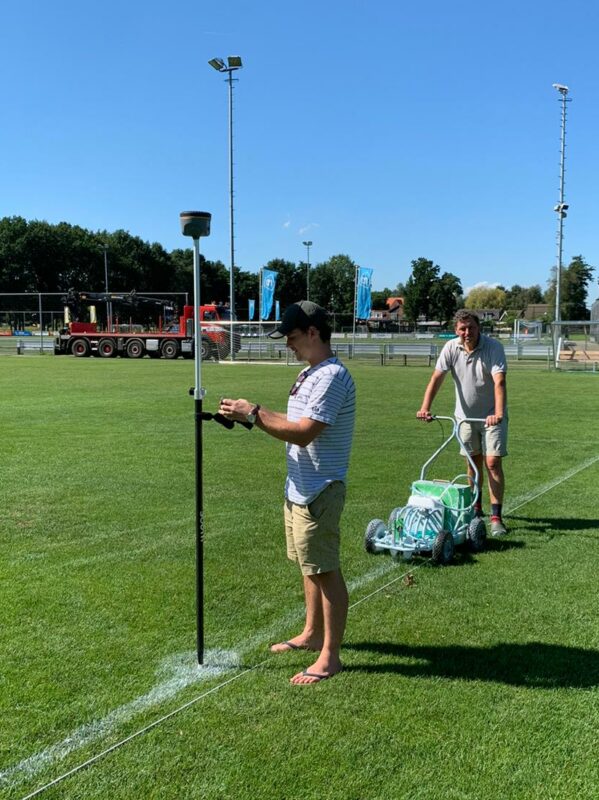
Surveying and Mapping
Surveyors and cartographers rely on SBAS to achieve high-precision positioning for accurate mapping and geospatial data collection. It enables them to create detailed and reliable maps, support land management activities, and contribute to urban planning and infrastructure development.
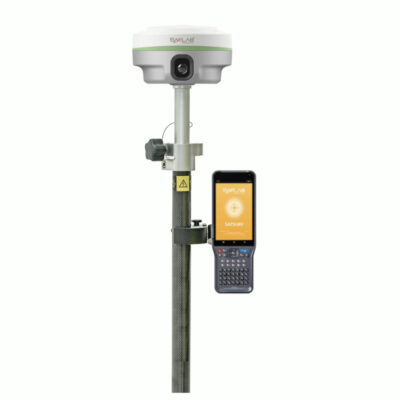
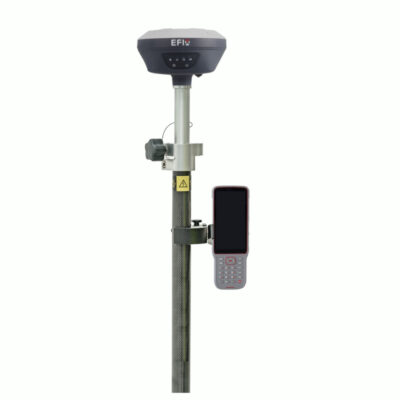
some popular gnss rover sets that support sbas
Conclusion
Satellite-Based Augmentation Systems (SBAS) have emerged as a vital tool for enhancing navigation accuracy across various industries. By providing real-time correction data for GNSS signals, SBAS significantly improves position accuracy, integrity monitoring, and availability. The benefits of SBAS extend to aviation, maritime, land transportation, and surveying, where it enhances safety, efficiency, and reliability. As technology continues to evolve, SBAS will play an increasingly critical role in our interconnected world, ensuring accurate and seamless navigation for a wide range of applications.









